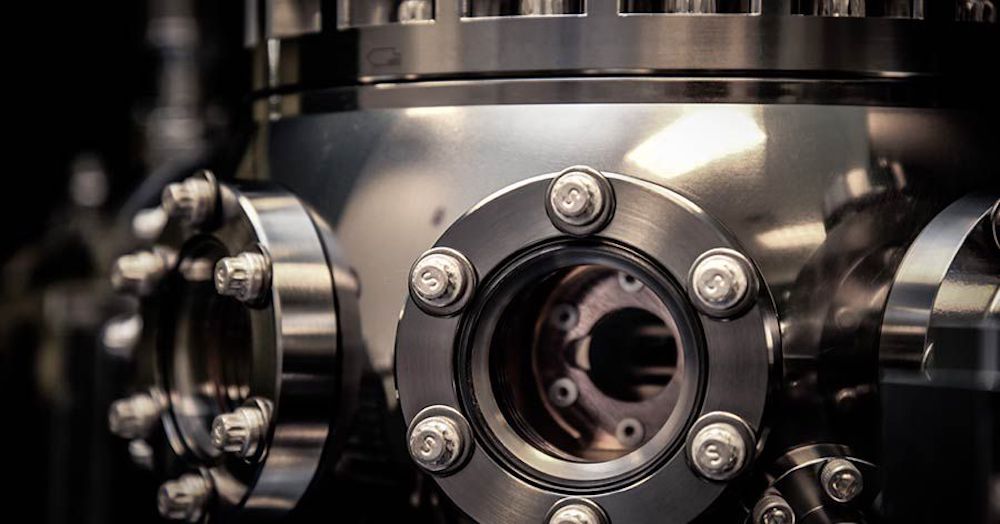

“The era of quantum computing is just beginning, and we are looking forward to bringing that capability to a broader audience,” said Tony Uttley, president of Honeywell Quantum Solutions.
Here are three to know:
1. What’s a ‘qubit’ and how it works
Computers traditionally use bits to process information. But quantum computing depends on bits that have properties of quantum physics – called qubits.
Traditional computing bits are either “0” or “1,” but qubits can be in both states at the same time, a quantum property called superposition.
Another quantum property, called entanglement, allows for qubits to be quantum mechanically connected to other qubits in the system.
As a result, quantum computers leverage entanglement and superposition to solve previously impossible computational problems.
2. How quantum computing will help industries tackle problems
Quantum computers will disrupt current techniques and solve previously unapproachable problems, creating valuable solutions for industry.
“For example, pharmaceutical companies could accelerate the discovery of new drugs, materials companies could discover new molecular structures, finance companies could develop new trading strategies, transportation companies could optimize logistics, and companies relying on the output of machine and deep learning could perform analyses that are impossible with classical computing of today,” Tony said.
Consider a few more industries that could benefit:
Quantum computing will enable industries to tackle problems they never would have attempted to solve before.
And the quantum computing market is projected to grow strongly through the next decade, according to a Tractica market report.
“Wide access is important as quantum computing makes its way into solving mainstream business problems,” Tony said. “Microsoft’s Azure Quantum platform provides another path for making sure we reach a broad audience.”
Here are three to know:
1. What’s a ‘qubit’ and how it works
Computers traditionally use bits to process information. But quantum computing depends on bits that have properties of quantum physics – called qubits.
Traditional computing bits are either “0” or “1,” but qubits can be in both states at the same time, a quantum property called superposition.
Another quantum property, called entanglement, allows for qubits to be quantum mechanically connected to other qubits in the system.
As a result, quantum computers leverage entanglement and superposition to solve previously impossible computational problems.
2. How quantum computing will help industries tackle problems
Quantum computers will disrupt current techniques and solve previously unapproachable problems, creating valuable solutions for industry.
“For example, pharmaceutical companies could accelerate the discovery of new drugs, materials companies could discover new molecular structures, finance companies could develop new trading strategies, transportation companies could optimize logistics, and companies relying on the output of machine and deep learning could perform analyses that are impossible with classical computing of today,” Tony said.
Consider a few more industries that could benefit:
- Airlines seeking the optimal way to store spare parts at airports.
- Distribution centers wanting the best way to maneuver robotics around a warehouse.
- Oil and gas companies calculating how atoms and molecules can be configured to protect equipment from corrosion.
- Ideal answers to these problems across industries could be found through quantum computing.
Quantum computing will enable industries to tackle problems they never would have attempted to solve before.
And the quantum computing market is projected to grow strongly through the next decade, according to a Tractica market report.
“Wide access is important as quantum computing makes its way into solving mainstream business problems,” Tony said. “Microsoft’s Azure Quantum platform provides another path for making sure we reach a broad audience.”



 IonQ Achieves Industry Leading Performance on Next Generation Barium Qubits
IonQ Achieves Industry Leading Performance on Next Generation Barium Qubits